Logical Fallacy Definition: A statement that appears to be logical but does not meet the requirements of valid logical arguments or induction.
SOME Logical Fallacies
Appeal to Authority – (Argument from Authority) If an authority, leader or expert says it is true, it must be true. That all depends on the authority, his knowledge of the subject, his agenda and his belief system. This argument goes: if Einstein or (fill in the blank) said it, then it must be true. Another form of this is the consensus of experts. Yes, a whole cadre of experts can be wrong if the framework (or paradigm) in which they believe is false or incomplete. Also, remember that being an expert in one field of science or being accomplished in any field does not qualify for expert status in another, sometimes related, field. We are all ignorant in more areas than those in which we are well versed. I wouldn’t want a physicist or engineer performing surgery on me, even if he is world renowned. Likewise, I wouldn’t want a surgeon to build a bridge. What makes a celebrity (or scientist or politician) more qualified than others to comment on issues of the day unless they are also experts in that field? Nothing.
Even experts can be wrong and their theories should never be sacrosanct against criticism or question. Could Einstein be wrong? Of course. Experts are not infallible, and treating them that way leads us back to protecting the status quo and COWDUNG[1]. One example from my past is a professor of zoology who insisted that holes found in pastures surrounding the college were due to pocket gophers. He had spent years studying them in the southwestern United States, so he could be considered an expert on pocket gophers. The college was in Virginia, well outside their range. The holes were due to ground hogs (wood chucks) which are common in the area. If you are a hammer, everything looks like a nail.
Appeal to Ignorance – (or argument from ignorance) This argument says that if a theory has not been proven wrong, it must be true. On the other hand, it can be argued that if the theory has not been proven true, it must be false. Or yet, if there is a lack of evidence for one theory, then another theory is assumed to be true. This is also called an Argument by Lack of Imagination. It can be applied to the arguments for macro-evolution[2]. In the sense that, because no one has come up with a different theory, which excludes God as a cause, then Darwin’s theory must be true. While there could be some validity in it, this is a specious[3] argument. Absence of another explanation does not make the current one true. The theory must rest on the evidence, not on an absence of an alternative theory or evidence to the contrary.
Argument from Silence – (argumentum ex silentio) Similar to Appeal to Ignorance; absence of evidence to the contrary or a different theory is deemed to validate the argument. Absence of evidence is not evidence of absence.
Argument from Personal Incredulity – A theory is thought to be proven untrue because someone finds it personally offensive, unlikely or unbelievable, and consequently a preferred alternative is thought to be proven true. Also known as Argument from Personal Belief or Argument from Personal Conviction.
Appeal to the Majority – Consensus as proof. A commonly held belief must be true. Consensus is an alien concept to science because it is based on opinion, assumption or belief not fact. Those advocating man-made global warming use this one profusely. They say the argument is over; it is a proven fact based on a supposed majority of scientists. Never mind that many of those included in the “consensus” know next to nothing about that field of study and many competent scientists in the field disagree or have doubts. Truth is never determined by committee vote or marketing or propaganda.
“In questions of science the authority of a thousand is not worth the humble reasoning of a single individual.” —- Galileo
Appeal to Emotion – Replacing rational arguments with emotional appeals. Propaganda is often laced with emotionally charged statements. Hitler was a master of this one.
False cause or non sequitur[4] – Incorrectly assumes that one thing is the cause or explanation of another; an argument where the conclusion does not connect well with the premise. Big trucks do not beget little trucks, although big (adult) animals beget little (infant) animals. City buses do not necessarily cause a reduction in the number of cars, especially when many buses are nearly empty or are scheduled poorly.
Irrelevant Conclusion – An argument for one conclusion really proves a different one. For example, arguments against Intelligent Design as not being science, but this argument can also be applied to Evolution itself.
Amphiboly – A sentence that can be interpreted in more than one way. Example: The statement, “He only said that.” could mean “only he” or “only said” or “only that.” Was he the only one saying it? Does it mean that he only said he would do it and that he didn’t actually do it? Does it mean he said only that and not the other statements attributed to him? As you can see, what is being modified by “only” makes a lot of difference.
Equivocation – Using the same term to mean two or more different things. Changing what is meant in mid-argument. This is commonly used in evolution’s defense where micro and macro-evolution are used interchangeably to defend the theory. Well documented variability within species is used in a confusing way to imply the ability of species to change into other species.
Changing the subject – Arguing for one thing to prove another. This is another favorite tool in evolution’s defense. Example: Using changes within a species as “proof” of evolution into an entirely different creature. See equivocation above.
Red Herring – inserting another unrelated factor intended to throw off the opposition rather than address the issue. Example: Citing the belief in seven literal days of Biblical creation to change the subject and/or discredit valid scientific objections to evolution.
Straw Man – arguing against a weaker proposition to imply winning a stronger one. Darwin set up his case for Evolution by arguing for repeated special creations from nothing. (God points and Poof! a new animal appears.) The prevailing view was really that changes had obviously happened through the ages, but that there was no evidence for a particular mechanism, divine or otherwise. Darwin didn’t provide a fact-based mechanism either, just opinions; but in light of this straw man argument, many found it plausible.
Ad Hominem Attack – attacking the opponent on personal grounds not related to the subject, including name calling or mischaracterizing the opponent’s beliefs. Example: Grouping people together to imply guilt by association to invalidate their arguments. Again, evolutionists group everyone who argues against Darwinian Evolution with young earth or seven-day creationists. This is also called guilt by association. Another form of this is maligning the opponent’s motives or character.
Begging the Question – The premise automatically assumes the truth of the conclusion in the statements to support it. Example: saying “Everyone knows—.” “There is a consensus among scientists that—-.” or “It has been proven—.”
Complex Question – The statement contains the conclusion within it.
Wrong Direction – An argument in which the cause and effect are reversed.
Post Hoc – because one thing follows another it is assumed to cause it. Example: According to statistics, people who smoke, drink alcohol and engage in sex at younger ages die younger, therefore early smoking, drinking and sex cause premature death. It does not take into account that this may imply a philosophy of risk taking and that the stated activity may have nothing to do with the causes of premature death, such as by accident, suicide or diabetes associated with extreme obesity and sedentary lifestyle.
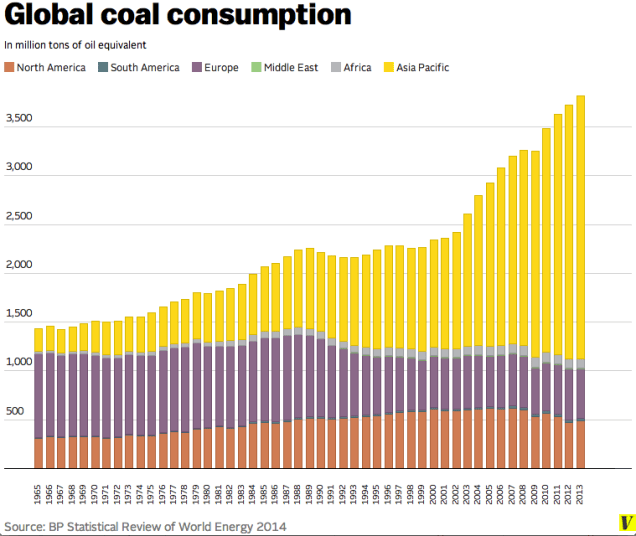
Insignificant or Complex Cause – one thing is assumed to cause another but it is only one, perhaps minor, part of a group of causes. Example: The assumption that man is the cause of global warming, when other factors such as changes in solar radiance, water vapor and clouds, methane from animals and decomposing vegetation, changes in surface reflectivity and the fact that we have been recovering from the Little Ice Age since the mid-1700s could be equally or more important.
Appeal to Motives: Prejudicial Language – value or moral goodness is attached to agreeing with the argument; conversely, assigning immoral or sinister motives to the opponent. Those opposed to the theory of man-made global warming are judged to have sinister motives that will harm mankind and the planet.
[1] COWDUNG – the COnventional Wisdom of the DomiNant Group, Michael Disney, The Hidden Universe, 1984
[2] Macro-evolution – that which gives rise to whole new species, as opposed to micro-evolution that describes variations within a single species. Micro-evolution is well known and has been applied successfully by breeders of everything from petunias to dogs.
[3] Specious – having a false appearance of truth or genuineness.
[4] Non sequitur – (Latin: it does not follow) an inference that does not follow from the premise.